In depth: MySQL 5.6+ DDL
Overview
DDL (Data Definition Language) statements create, alter, and remove database objects. These types of changes can be a very dangerous action to take on such a critical piece of your infrastructure. You want to make sure that the command that you are executing has been given proper thought and testing. In this post I go through multiple version of MySQL and verify the best course of action to take in regards to executing DDL statements. There are many things that you have to consider when making these types of changes, such as disk space, load on the database server, slave replication, the type of DDL statement you are executing, and if it will lock the table. Because of these risks, there are tools that can be used to help mitigate some of the dangers. But unless you have tested and verified their functionality, these tools in themselves can cause trouble. Whenever in doubt, take the time to test and verify any changes that you will make. In my testing I will be using :- MySQL 5.6+ Inherent Online DDL
- pt-online-schema-change
- Overview of Online DDL
- Examples of Online DDL
- Limitations of Online DDL
The Setup
All of my testing was done in virtual machines (VMs) on my laptop. I have a VM that will be running mysqlslap to perform remote DML statements such as SELECT, UPDATE, DEELTE and INSERT, causing load on the database server. This will allow me to see any potential table locks or performance impact. Here is the setup of the MySQL machine and it's components. I have created the table shown below and imported 10 million rows. While mysqlslap was running I performed each of the DDL statements and watched that the DML statements were being executed with no table locks. I then recorded the time as they completed.MySQL Server Stats
- CPU : 4x CPUs at 2.6 GHz Intel Core i7
- Memory allocated to VM : 2 Gig
- Memory allocated to MySQL Innodb buffer pool: 1 Gig
- Flash Storage
- Table has 10 Million Rows.
- DML (Data Manipulation Language) statements such as select, insert, update, and delete, that will be executed against the table during DDL statements
Table Structure
[code lang="sql"] CREATE TABLE `employee_test` ( `emp_no` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `birth_date` date NOT NULL, `first_name` varchar(14) NOT NULL, `last_name` varchar(16) NOT NULL, `gender` enum('M','F') NOT NULL, `hire_date` date NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`emp_no`), KEY `ix_lastname` (`last_name`), KEY `ix_firstname` (`first_name`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=10968502 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 [/code]MySQL DDL Commands
[code lang="sql"] CREATE INDEX ix_hire_date ON employee_test (hire_date); --CREATE INDEX CREATE FULLTEXT INDEX ix_lastname_fulltext ON employee_test(last_name); --CREATE FULLTEXT INDEX DROP INDEX ix_hire_date ON employee_test; --DROP INDEX OPTIMIZE TABLE employee_test; --OPTIMIZE TABLE ALTER TABLE employee_test ADD COLUMN test_column INT NULL; --ADD COLUMN ALTER TABLE employee_test DROP COLUMN f_name; --DROP COLUMN ALTER TABLE employee_test CHANGE first_name f_name varchar(14) NOT NULL; --RENAME COLUMN ALTER TABLE employee_test MODIFY COLUMN emp_no BIGINT AUTO_INCREMENT NOT NULL; --CHANGE COLUMN TYPE [/code]pt-online-schema-change DDL Commands
[code lang="bash"] pt-online-schema-change --execute --alter 'ADD FULLTEXT INDEX ix_lastname_fulltext (last_name)' D=employees,t=employee_test pt-online-schema-change --execute --alter 'ENGINE=INNODB' D=employees,t=employee_test pt-online-schema-change --execute --alter 'ADD COLUMN test_column3 INT NULL' D=employees,t=employee_test pt-online-schema-change --execute --alter 'MODIFY COLUMN gender BLOB NULL' D=employees,t=employee_test [/code]Results
This matrix is a representation of the testing that I performed and how quickly the commands took to execute. Be careful with Fulltext indexes on your tables since they potentially can cause additional locking by creating the necessary infrastructure in the background. Please see MySQL Innodb Fulltext Indexes for more details. This requirement causes a great deal of locking on the table.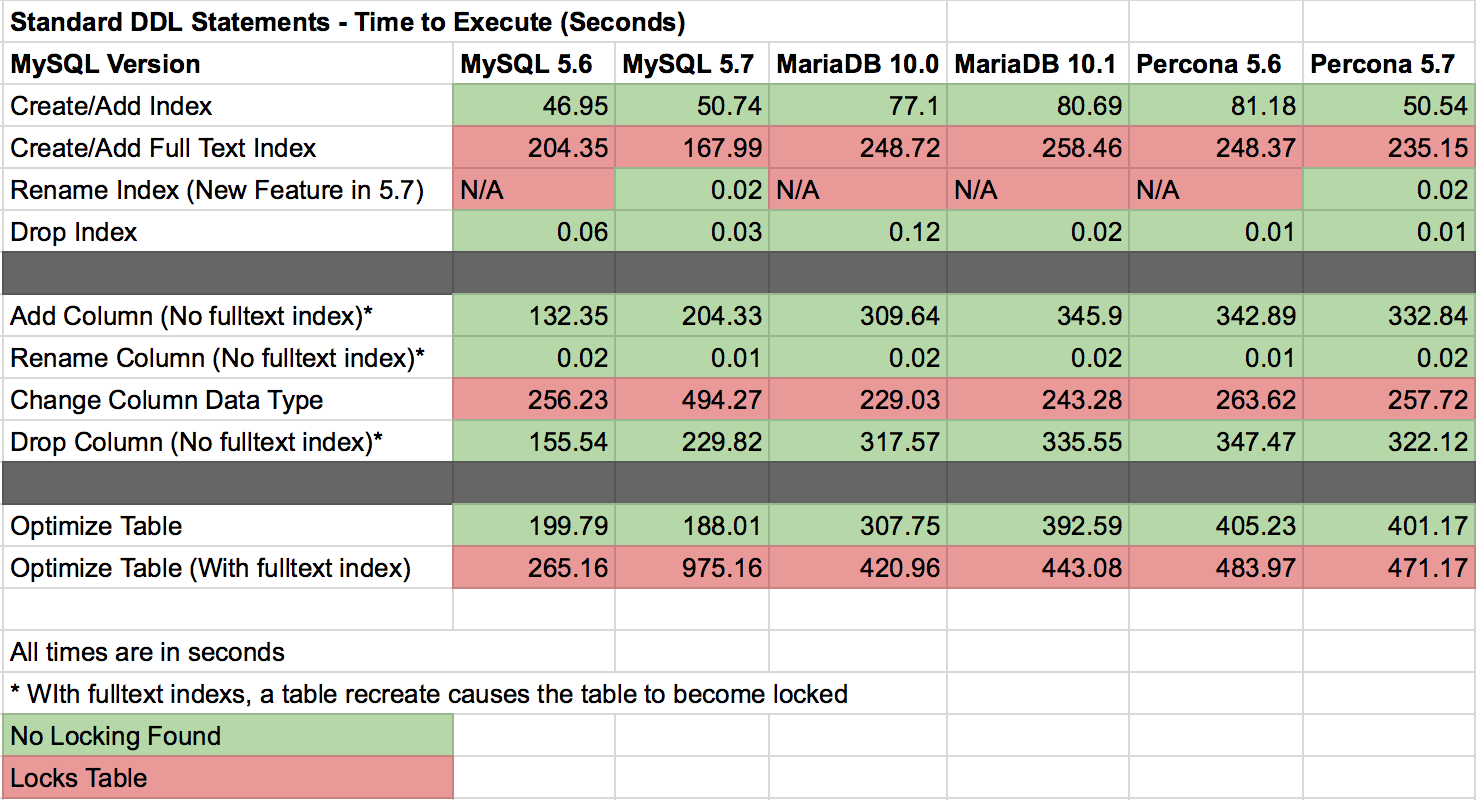
pt-online-schema-change
For the DDL statements that cause locking of the table we wanted to look at incorporating pt-online-schema-change, to help us overcome this obstacle.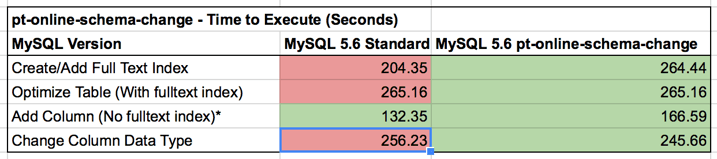 pt-online-schema-change allowed us to perform the operations that locked the table previously with no locking. pt-onilne-schema-change also has many other features such as helping with the impact on slave replication, and handling foreign keys. But it also has it's limitation such as not being able to run it on a table that already has triggers, or complications with foreign keys. There are also impacts on your environment if it is not properly tested and verified. One such example is, every time that I ran pt-online-schema-change in my test it caused a deadlock causing mysqlslap to die and no longer perform and further statements.
pt-online-schema-change allowed us to perform the operations that locked the table previously with no locking. pt-onilne-schema-change also has many other features such as helping with the impact on slave replication, and handling foreign keys. But it also has it's limitation such as not being able to run it on a table that already has triggers, or complications with foreign keys. There are also impacts on your environment if it is not properly tested and verified. One such example is, every time that I ran pt-online-schema-change in my test it caused a deadlock causing mysqlslap to die and no longer perform and further statements.
mysqlslap: Cannot run query UPDATE employee_test SET first_name = ‘BigPurpleDog’ WHERE last_name = ‘SmallGreenCat’; ERROR : Deadlock found when trying to get lock; try restarting transactionThis is why it is very important to try and determine the impact if any that pt-online-schema-change may have on your environment before starting to use it. I did not encounter this behavior with any of the MySQL DDL statements that I ran.
Performance Impact
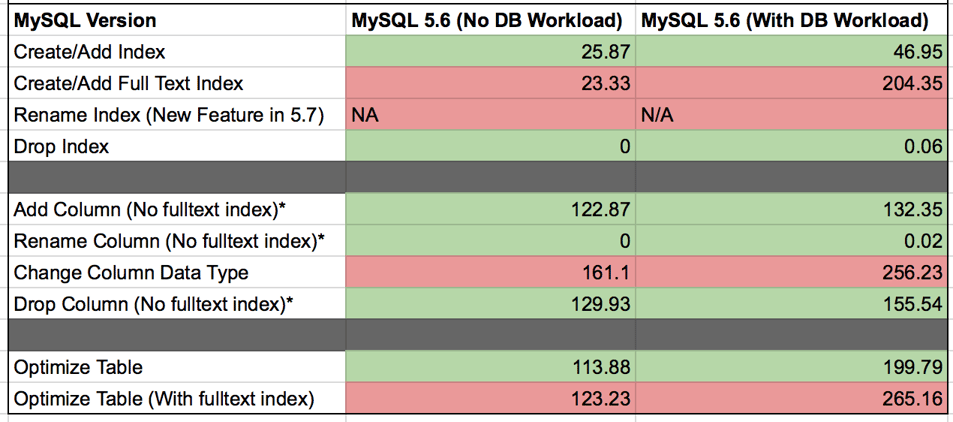
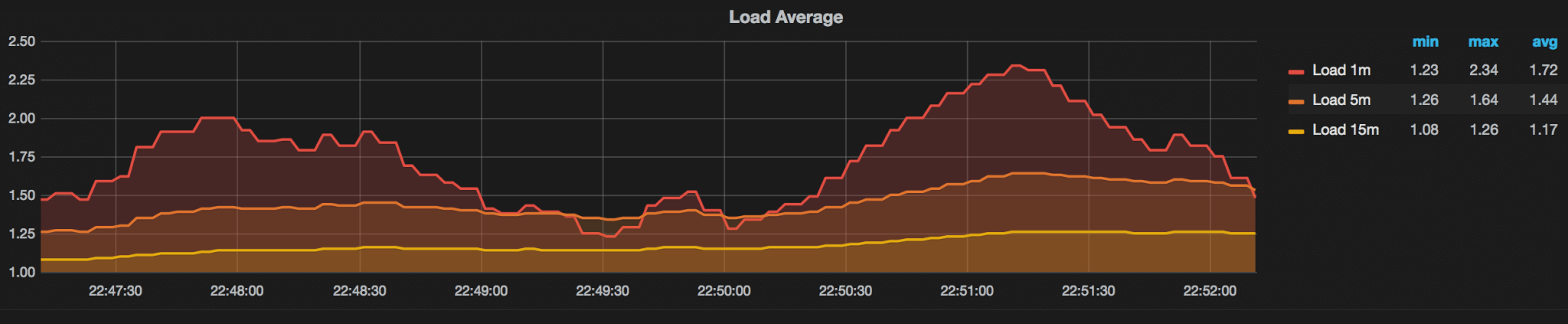
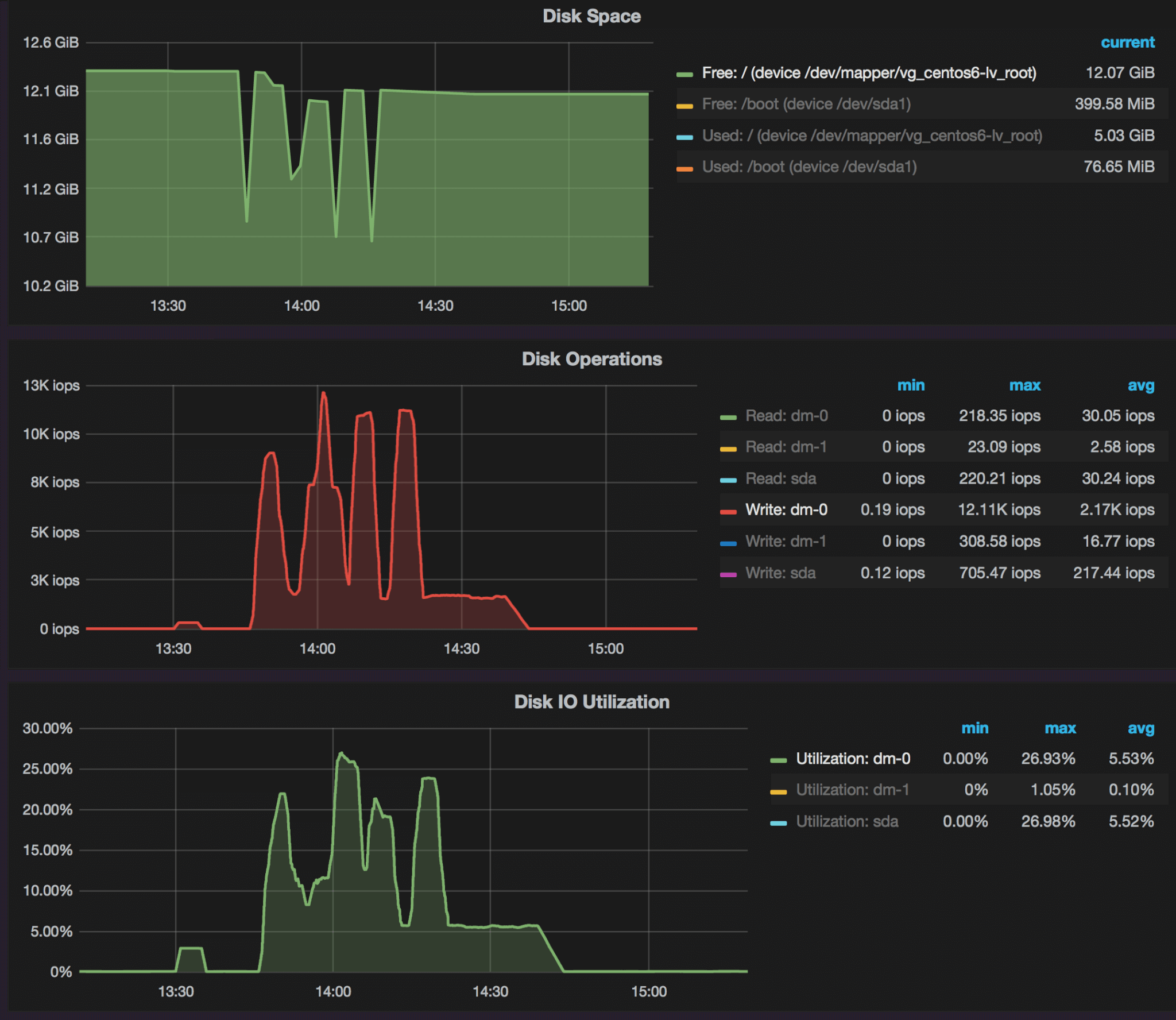
While performing the changes there were consistent increases in CPU load, disk I/O, and disk usage as the new tables were being created for the table alters. We have to remember that when certain DDL statements are being executed, a full copy of the table is being performed, so you will want to make sure you have enough disk space to complete the change. This is why it is very important to take into consideration the size of the table you are altering and the load on the MySQL server while performing DDL statements. It is preferred that you run any of the DDL statements that cause table copies, off hours as to avoid any delays or outages to the application that is using the data.Query Execution Impact
Server Performance Impact
Conclusion
As I have observed in performing these tests, there are many things to consider when performing DDL statements to avoid potential downfalls. Here is a summary of the recommendations to executing DDL statements or using pt-online-schema-change. Before considering any of this determine if the statement you are going to perform is going to copy a table, and if it does, make sure you have enough disk space.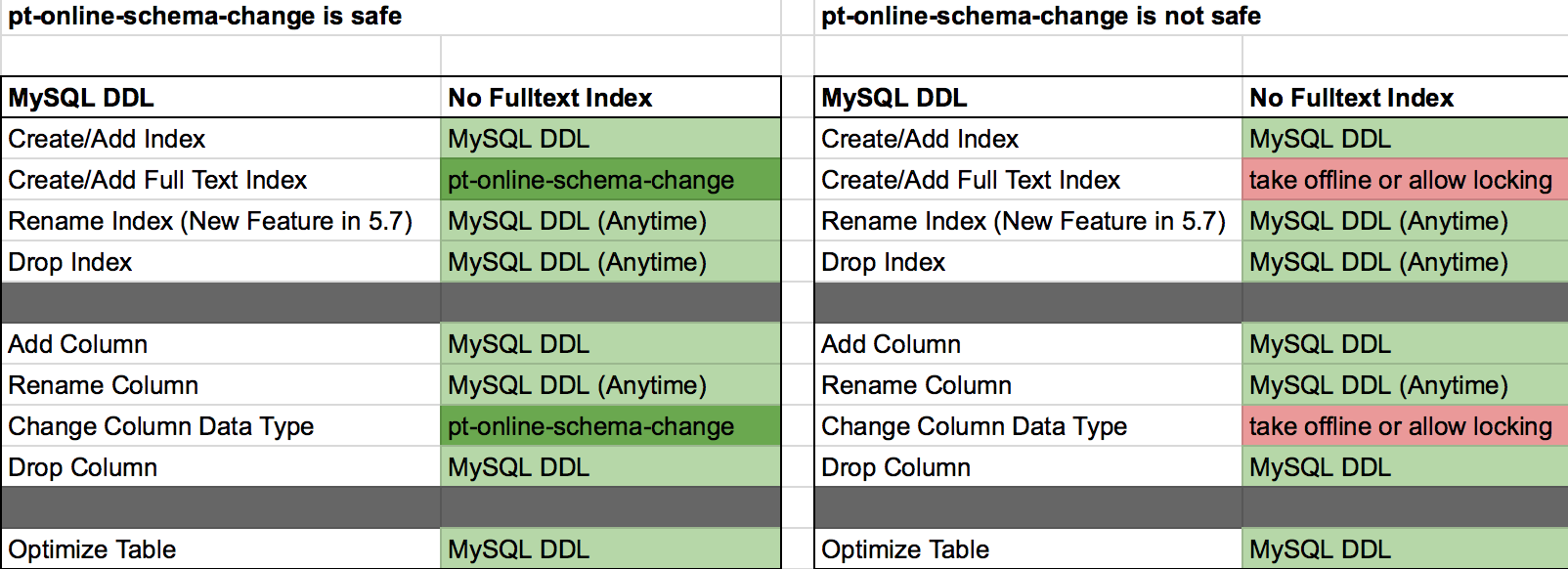
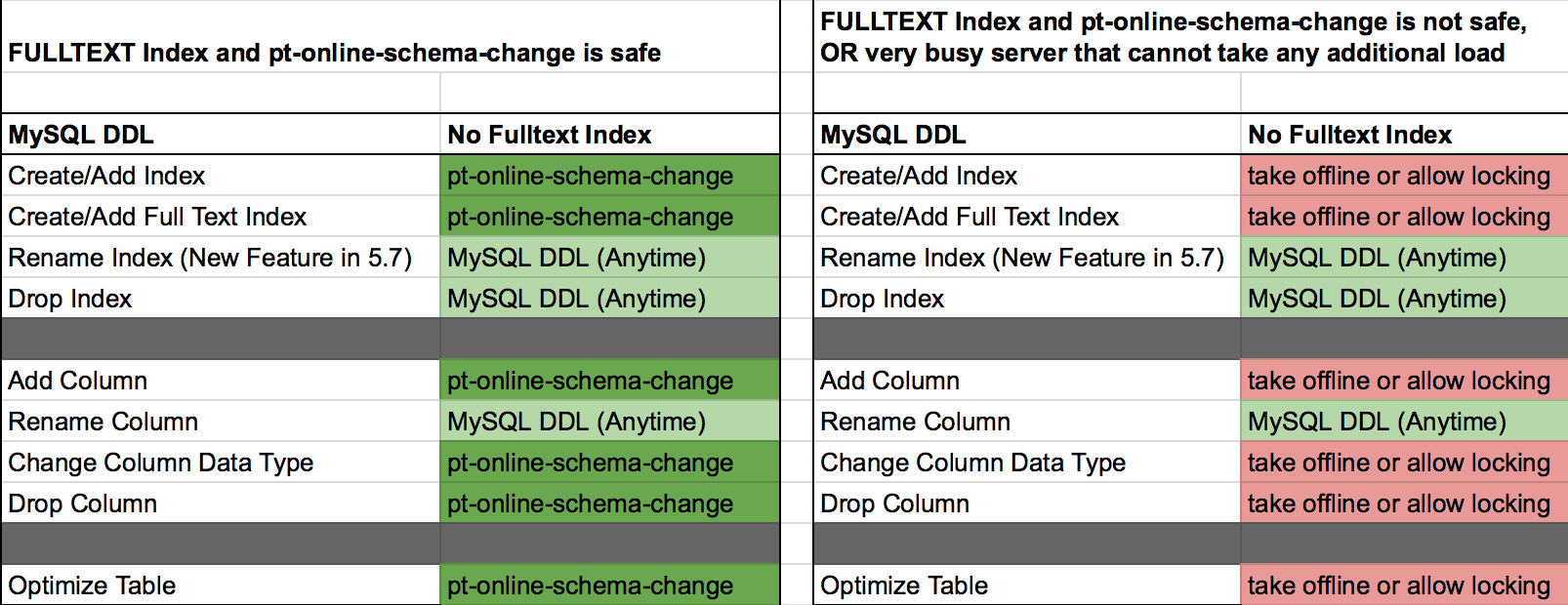 If you are going to make changes to your production servers, make sure that you run your DDL statements during off hours when the server is at it's lowest utilization for both CPU and disk. For an added safety measure when you are performing any of the MySQL DDL statements that you are expecting to be executed INPLACE and will not lock the table, make sure you specify ALGORITHM=INPLACE in your statement. If MySQL is unable to execute the command in place, it will just return an error, instead of executing the statement with the COPY algorithm which will lock the table. Here are samples of the DDL statements that you should be able run INPLACE and not cause any locking of your table. [code lang="sql"] ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, ADD INDEX ix_hire_date (hire_date); --CREATE INDEX ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, DROP INDEX ix_firstname; --DROP INDEX ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, ENGINE=INNODB; --OPTIMIZE TABLE ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, ADD COLUMN test_column INT NULL; --ADD COLUMN ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, DROP COLUMN f_name; --DROP COLUMN ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, CHANGE first_name f_name varchar(14) NOT NULL; --RENAME COLUMN [/code]
If you are going to make changes to your production servers, make sure that you run your DDL statements during off hours when the server is at it's lowest utilization for both CPU and disk. For an added safety measure when you are performing any of the MySQL DDL statements that you are expecting to be executed INPLACE and will not lock the table, make sure you specify ALGORITHM=INPLACE in your statement. If MySQL is unable to execute the command in place, it will just return an error, instead of executing the statement with the COPY algorithm which will lock the table. Here are samples of the DDL statements that you should be able run INPLACE and not cause any locking of your table. [code lang="sql"] ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, ADD INDEX ix_hire_date (hire_date); --CREATE INDEX ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, DROP INDEX ix_firstname; --DROP INDEX ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, ENGINE=INNODB; --OPTIMIZE TABLE ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, ADD COLUMN test_column INT NULL; --ADD COLUMN ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, DROP COLUMN f_name; --DROP COLUMN ALTER TABLE employee_test ALGORITHM=INPLACE, CHANGE first_name f_name varchar(14) NOT NULL; --RENAME COLUMN [/code]
References
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/innodb-online-ddl.html
- https://jordan.broughs.net/images/days-since-drop-production.png
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/innodb-create-index-overview.html
- https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/innodb-create-index-overview.html
- https://www.percona.com/doc/percona-toolkit/2.2/pt-online-schema-change.html
- https://launchpad.net/test-db/
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/25858069/in-mysql-5-6-whats-the-default-behavior-of-the-algorithm-parameter
On this page
Share this
Share this
More resources
Learn more about Pythian by reading the following blogs and articles.
How to delete an RAC Database Using DBCA silent mode
![]()
How to delete an RAC Database Using DBCA silent mode
Aug 12, 2019 12:00:00 AM
2
min read
Getting started with Oracle Database Backup Service in 2018
![]()
Getting started with Oracle Database Backup Service in 2018
Aug 3, 2018 12:00:00 AM
7
min read
Building an ETL Pipeline with Multiple External Data Sources in Cloud Data Fusion


Building an ETL Pipeline with Multiple External Data Sources in Cloud Data Fusion
Aug 23, 2022 12:00:00 AM
12
min read
Ready to unlock value from your data?
With Pythian, you can accomplish your data transformation goals and more.
